How Countable Uses GIT¶
Purpose
Outlining the norms of git collaboration at Countable.
Scope
Broad coverage of multiple elements of git workflow.
Git Branches¶
Countable uses git flow for branch naming.
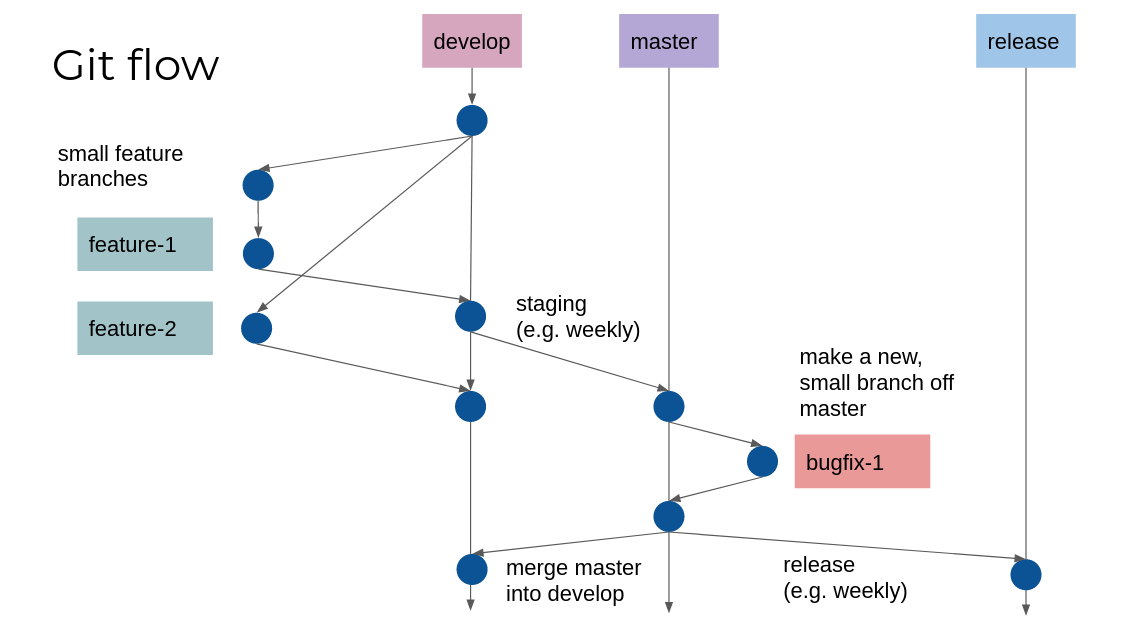
developis the main branch developers work on and test.masteris the stable branches released to production. (most projects do not use release branches, we just continuously deploymaster)feature/my-feature-namefeature branches contain your work for up to one day, before being merged back intodevelop.hotfix/my-bug-namehotfix branches are merged intomasterto fix urgent problems in production.
Our feature branches are owned by a single person and very short-lived,see trunk based development. From the latter:
You should do Trunk-Based Development instead of GitFlow and other branching models that feature multiple long-running branches. You can either do a direct to trunk commit/push (v small teams) or a Pull-Request workflow, as long as those feature branches are short-lived and the product of a single person.
Contributing To A Project¶
- Check out
developand make a branch from that.
git checkout develop
git checkout -b feature/fireball-spell
- Do your work, commit, update, push.
git commit -a -m "Added the Fireball ability to wizards, Trello ticket #51"
git pull origin develop
git push origin feature/fireball-spell
(Git will print out a link in the terminal that you may open to quickly create a pull request.)
- Test that your changes dont’t break anything.
Run automated tests and check things you know other team members are actively working on still work.
- Submit a pull request from
fireball-spelltargetingdevelop.
Another developer on the project should review and comment on your changes. When everyone agrees, anyone can merge the changes. The fireball-spell branch is then deleted after being merged.
Hotfix¶
If production is broken, you want to fast-track a fix into master. Only for emergencies. Your PR will be made against master instead of develop in this case.
General GIT Guidelines¶
- Commit often (~hourly), with each logical change in its own commit. If for no other reason, developers who commit multiple times per day are nearly 10% more likely to be satisfied with their jobs (Stack Overflow dev survey, 2017). That’s one crazy correlation for such a simple behaviour!
- Push often, and merge into
developevery day. You will need to structure your work in a way that avoids long-lived branches: Use feature flags, comment out broken tests, leave “TODO” notes, and hide functionality in the UI if it’s not ready yet. - Use the “imperative voice” for commit messages: Verb noun. ie) “Remove magic glyphs from wizard profile card.”
- Don’t commit example code. Remove or gitignore it.
- Don’t commit commented code, unless you have another English comment above it explaining why it’s commented out, and not deleted.
- Use Trunk Based Development. Your feature branches should be merged into
developwithin a day of being created. - Unfinished things (links that go nowhere, or Lorem Ipsum) we don’t want to show up live should be deleted, fixed, or commented out. Leave an additional comment indicating why they’re commented out if you do the latter. These things are fine to commit, but before you do a Pull Request, please review your own code and clean it up so it’s something you’re proud to show your team.
- When merging, check you’ve not missed any merge markers still in unmerged files.
grep -r ">>>>>" .will normally do this for you for example. - We use the “monorepo” pattern, which means it’s better to have one large repo for an entire project. Not multiple small ones for components.
- Be careful when merging in the upstream (develop) branch that you don’t overwrite anyone else’s changes with yours. It pays to look closely at each merge marker. Use a 3way merge tool
git mergetoolif the merge is nontrivial.
Tips for Creating A Pull Request¶
When you create your pull request:
- Review it on BitBucket yourself because it lets you find embarassing mistakes without your team seeing them ;)
- Comment on specific lines you want the reviewer to notice.
- Check the checkbox option to automatically delete the branch after merge. You can merge right away, no approval required.
- Code reviews are not a gate for deployment. The submitter merges the code at any time based on the team’s needs. Communicate about what you’re doing. If code is merged before you review, the reviewer can still add comments and changes can be patched in as needed.
- Do not merge unless the tests are passing. Don’t break the tests in
develop. If you do, fix them ASAP because other devs will be unable to test their work otherwise.
Tips for Code Reviews¶
When a pull request is created, several people are set to automatically review.
- The main goal of code reviews is for everyone to learn from each other. So, ask your questions and discuss using the pull request comments!
- It’s a good idea to review code within 2 days of it being written, because then the author has it fresh in their mind and can make corrections easily based on your suggestions.
- It’s up to the reviewer’s judgement how much time they spend on a code review. It could be quick or more in-depth.
- The reviewer should understand what the code is doing. If it’s unclear, ask in a review comment what it does.
- Reviewer should point out anything that’s not following project conventions. Are we doing something a new way, when a perfectly good way existed before?
- Try to find and remove any duplicate code (DRY) or dead code.
- Review these Code Review Guidelines
- If you review code, always indicate you did so. Either click “approve”, or leave a comment.